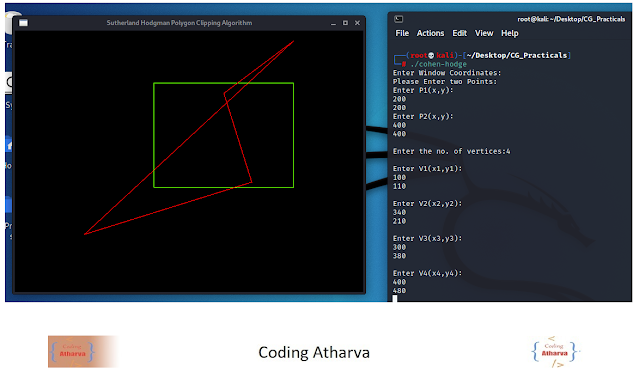
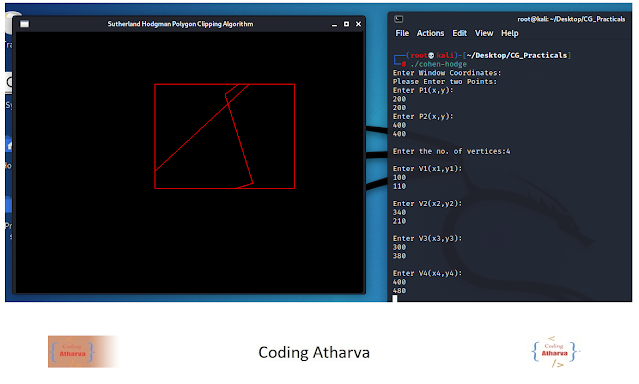
Program:
// Sutherland Hodgman Polygon Clipping Complete Code | implementation through openGL
#include <stdio.h>
#include <GL/gl.h>
#include <GL/glu.h>
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef struct // structure that holds the information of points
{
float x;
float y;
} PT;
// global variables
int n;
int i, j;
PT p1, p2, p[20], pp[20];
void left() // left clipper
{
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (p[i].x < p1.x && p[i + 1].x >= p1.x) //Case-1: outside to inside
{
if (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x != 0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) / (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) * (p1.x - p[i].x) + p[i].y; // save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p1.x;
j++;
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x; // save that point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y;
j++;
}
if (p[i].x >= p1.x && p[i + 1].x >= p1.x) //Case-2: inside to inside
{
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y; // only save second point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x;
j++;
}
if (p[i].x >= p1.x && p[i + 1].x < p1.x) // Case-3: inside to outside
{
if (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x != 0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) / (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) * (p1.x - p[i].x) + p[i].y; // only save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p1.x;
j++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n = j;
}
void right() // right clipper
{
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (p[i].x > p2.x && p[i + 1].x <= p2.x) //Case-1: outside to inside
{
if (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x != 0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) / (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) * (p2.x - p[i].x) + p[i].y; // save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p2.x;
j++;
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x; // save that point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y;
j++;
}
if (p[i].x <= p2.x && p[i + 1].x <= p2.x) // Case-2: inside to inside
{
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y; // only save second point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x;
j++;
}
if (p[i].x <= p2.x && p[i + 1].x > p2.x) // Case-3: inside to outside
{
if (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x != 0)
{
pp[j].y = (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) / (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) * (p2.x - p[i].x) + p[i].y; // only save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].y = p[i].y;
}
pp[j].x = p2.x;
j++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
}
void top() // top clipper
{
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (p[i].y > p2.y && p[i + 1].y <= p2.y) //Case-1: outside to inside
{
if (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y != 0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) / (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) * (p2.y - p[i].y) + p[i].x; // save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p2.y;
j++;
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x; // save that point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y;
j++;
}
if (p[i].y <= p2.y && p[i + 1].y <= p2.y) // Case-2: inside to inside
{
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y; // only save second point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x;
j++;
}
if (p[i].y <= p2.y && p[i + 1].y > p2.y) // Case-3: inside to outside
{
if (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y != 0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) / (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) * (p2.y - p[i].y) + p[i].x; // only save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p2.y;
j++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n = j;
}
void bottom() // bottom clipper
{
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (p[i].y < p1.y && p[i + 1].y >= p1.y) // Case-1: outside to inside
{
if (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y != 0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) / (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) * (p1.y - p[i].y) + p[i].x; // save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p1.y;
j++;
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x; // save that point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y;
j++;
}
if (p[i].y >= p1.y && p[i + 1].y >= p1.y) // Case-2: inside to inside
{
pp[j].x = p[i + 1].x; // only save second point that lie inside our clipping window // consult theory
pp[j].y = p[i + 1].y;
j++;
}
if (p[i].y >= p1.y && p[i + 1].y < p1.y) // Case-3: inside to outside
{
if (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y != 0)
{
pp[j].x = (p[i + 1].x - p[i].x) / (p[i + 1].y - p[i].y) * (p1.y - p[i].y) + p[i].x; // only save point of intersection
}
else
{
pp[j].x = p[i].x;
}
pp[j].y = p1.y;
j++;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
p[i].x = pp[i].x;
p[i].y = pp[i].y;
}
p[i].x = pp[0].x;
p[i].y = pp[0].y;
n = j;
}
void drawpolygon()
{
glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2d(p[i].x, p[i].y);
glVertex2d(p[i + 1].x, p[i + 1].y);
glEnd();
}
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2d(p[i].x, p[i].y);
glVertex2d(p[0].x, p[0].y);
glEnd();
}
void myMouse(int button, int state, int x, int y)
{
if (button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) // On output, please left click on polygon then and only then clipping performs
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
glVertex2f(p1.x, p1.y);
glVertex2f(p2.x, p1.y);
glVertex2f(p2.x, p2.y);
glVertex2f(p1.x, p2.y);
glEnd();
left();
right();
top();
bottom();
drawpolygon();
}
glFlush();
}
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glColor3f(0.4, 1.0, 0.0);
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
glVertex2f(p1.x, p1.y);
glVertex2f(p2.x, p1.y);
glVertex2f(p2.x, p2.y);
glVertex2f(p1.x, p2.y);
glEnd();
drawpolygon();
glFlush();
}
void init(void)
{
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); // clear screen usually black
gluOrtho2D(0, 500, 0, 500);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("Enter Window Coordinates:\n");
printf("Please Enter two Points:\n"); // P1(x,y) is the bottom left point for clipping window
printf("Enter P1(x,y):\n");
scanf("%f", &p1.x); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter 200
scanf("%f", &p1.y); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter 200
printf("Enter P2(x,y):\n"); // P2(x,y) is the top right point for clipping window
scanf("%f", &p2.x); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter 400
scanf("%f", &p2.y); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter 400
printf("\nEnter the no. of vertices:"); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter 3
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("\nEnter V%d(x%d,y%d):\n", i + 1, i + 1, i + 1);
scanf("%f", &p[i].x); // if you don't know what value should be given: enter V1(100,110), V2(340,210), V3(300,380)
scanf("%f", &p[i].y);
}
p[i].x = p[0].x; // Assign last to first for connected everything
p[i].y = p[0].y;
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(640, 480);
glutInitWindowPosition(0, 0);
glutCreateWindow("Sutherland Hodgman Polygon Clipping Algorithm ");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMouseFunc(myMouse); // notice mouse movement and call user defined function
glFlush();
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
Output:Before Clip: